
Sep 8, 2025 | Teacher Tips
This blog was last updated on 8 September 2025
This blog is presented by Twin Science, a global education technology company empowering educators through AI-enhanced learning solutions.
Why Are Ethical Dilemmas Emerging in AI Use for Education?
As AI becomes a regular presence in classrooms, it doesn’t just raise hopes, it raises questions. Teachers ask: Is it fair for an algorithm to guide student progress? Who ensures privacy? What happens if bias creeps in?
These aren’t just technical issues; they’re ethical dilemmas. And for educators already balancing tight schedules, the uncertainty around AI use can feel overwhelming.
This is why exploring AI in education requires more than knowing how tools work, it demands understanding the values behind them. With classroom-ready AI tools designed for equity, safety, and pedagogy, you don’t have to navigate this gray space alone.
Get in contact to discover classroom-ready AI learning solutions built with teachers’ needs and students’ rights in mind.

What Are the Main Ethical Challenges in AI Use?
Educators often face three gray areas when adopting teacher AI tools:
1- Bias & Fairness: Does the AI treat all students equally, regardless of background or ability?
2- Data Privacy: How is sensitive student information protected? Who has access?
3- Transparency: Can teachers and students understand how AI makes its decisions?
These concerns aren’t abstract, they affect daily teaching. For instance, an AI system that recommends math exercises may unintentionally assign harder tasks to some groups of students while giving fewer opportunities to others. Without oversight, such tools risk reinforcing inequities.
How Can Teachers Navigate These Ethical Dilemmas?
The key is not rejecting AI, but using it wisely. Ethical AI use in education often means:
-
Human-in-the-loop: Keeping teacher judgment central, using AI insights as guidance, not replacement.
-
Clear boundaries: Setting transparent rules on what data is collected and how it’s used.
-
Inclusive design: Choosing tools that adapt to diverse learning needs and reflect a wide range of student experiences.
Research suggests that AI has the potential to foster inclusion when thoughtfully applied. That means educators play a vital role: asking questions, monitoring outcomes, and ensuring technology supports, not dictates, the learning journey.
Start using AI tools designed to save time while keeping you in control of ethical decisions in your classroom.

How Does This Align With Twin’s Learning Vision?
At Twin Science, we believe education isn’t just about building skills; it’s about building conscience. Our vision of a double-winged generation emphasizes not only competence in STEM but also a sense of social responsibility.
AI should reflect this balance. A student who uses an AI-powered simulation to explore renewable energy isn’t just learning science, they’re also developing empathy for the planet. Ethical use of AI means helping children grow into innovators who create with both skill and conscience.
Where Do We Go From Here?
The ethical gray areas of AI in education won’t vanish overnight. But they don’t need to paralyze progress either. By asking tough questions, setting boundaries, and choosing responsible edtech learning solutions, you can make AI a trusted ally.
It’s time to move beyond “Is AI safe?” and toward: “How can AI help us raise learners who are skilled, fair, and socially conscious?”
Get your classroom started with hands-on AI tools today, and navigate the gray areas with confidence.

Sep 8, 2025 | Teacher Tips
This blog was last updated on 8 September 2025
This blog is presented by Twin Science, a global education technology company empowering educators through AI-enhanced learning solutions.
Why Do Teachers Struggle to Measure AI’s Impact?
Educators are adopting AI tools faster than ever, yet many quietly wonder: Is this really improving learning, or just adding more noise to my workload? The truth is, measuring AI’s educational impact is complex. Traditional metrics like test scores or attendance don’t capture the deeper changes AI brings to classrooms, like how it sparks curiosity, nurtures critical thinking, or personalizes learning.
This is where you might feel stuck. You’re investing effort, but the benefits aren’t always visible. That’s why exploring classroom-ready AI tools designed for real pedagogical needs can make a difference. With Twin’s learning solutions, you see impact reflected not just in data, but in how students engage, question, and grow.
Discover hands-on AI learning solutions to make your classroom results measurable and meaningful.
What Should We Really Measure With AI in Education?
When considering AI in education, it helps to look beyond grades. Research suggests that AI’s value shines in three areas:
1- AI Literacy: Are students gaining skills to critically use and question AI?
2- Engagement & Curiosity: Do students show more interest in STEM topics through interactive, hands-on learning?
3- Equity & Inclusion: Does AI help close learning gaps by adapting to individual needs?
Measuring these outcomes requires a mix of teacher observation, student self-reflection, and long-term project-based results—not just standardized testing.
For example, an AI-powered quiz that adapts to student answers can reveal growth in real time. A simulation that connects science to climate action may not boost test scores immediately but builds future-ready problem-solving skills.

How Can You Track AI’s Impact Without Extra Workload?
One of the main teacher pain points is workload. Adding another tool often feels like adding another burden. The good news: effective teacher AI tools simplify, not complicate.
-
Automatic insights from quizzes or simulations save you hours of grading.
-
Built-in progress dashboards show learning growth over weeks, not just single tests.
-
Hands-on projects tied to STEM make learning visible. Students can present, reflect, and connect concepts to real life.
As AI becomes a daily part of student life, it’s essential to equip classrooms with tools that track progress in meaningful, low-effort ways.
Get in contact to start using AI tools that highlight growth while saving you time in the classroom.
How Does This Connect to Twin’s Learning Vision?
At Twin Science, we believe impact isn’t only about scores. It’s about raising what we call a double-winged generation: young people who are competent in STEM and guided by conscience.
That means AI’s impact should be seen in how children apply knowledge to real problems, collaborate with peers, and grow as socially conscious innovators. When you watch a child light up because they’ve used a coding activity to solve a sustainability challenge, you’re seeing impact beyond numbers, you’re seeing the future.
This is the kind of learning AI should unlock: personalized, applied, and socially responsible.

Where Do We Go From Here?
The challenge of measuring AI’s educational impact won’t disappear overnight. But with the right approach, you can capture outcomes that truly matter: curiosity, critical thinking, and confidence.
It’s time to shift the focus from “Is AI making test scores rise?” to “Is AI helping students grow as learners and changemakers?”
Elevate your classroom today.
Sep 3, 2025 | Teacher Tips
Twin Educatos’ Spotlight: Issue 29
Everything you need for the first week is here: a complete AI curriculum, quizzes that turn into competitions, and a comprehensive back-to-school guide! With Twin, you save time and step into class ready, supported by resources we build together with educators like you. Don’t forget to claim your gift at the end of this newsletter! 🎁
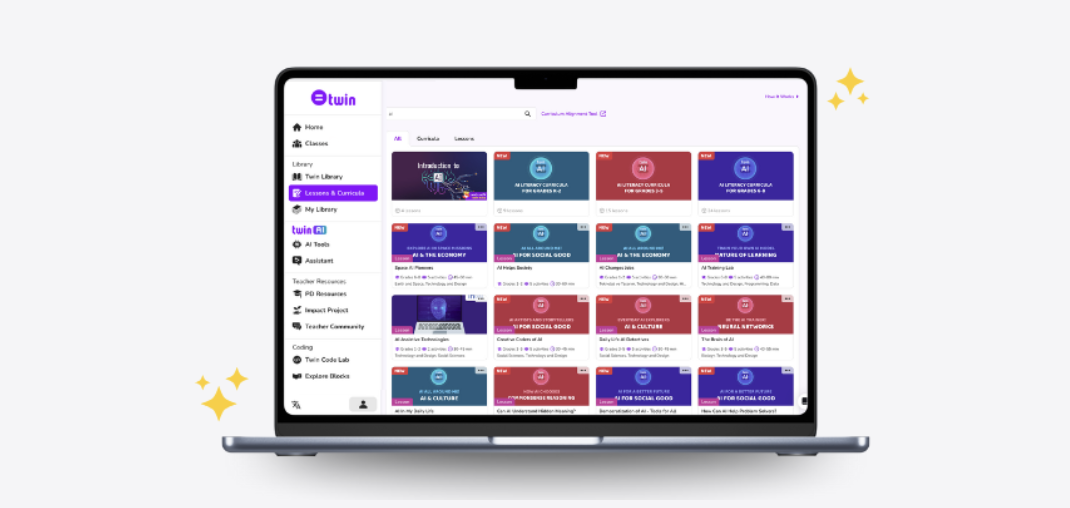
💻 AI Curriculum on Twin

New term starting and wondering about teaching AI? We’ve got a full AI literacy curriculum covering all primary and secondary years available on the Twin Educator Platform.
Explore AI Curriculum >
✅ The First Week in 3 Steps
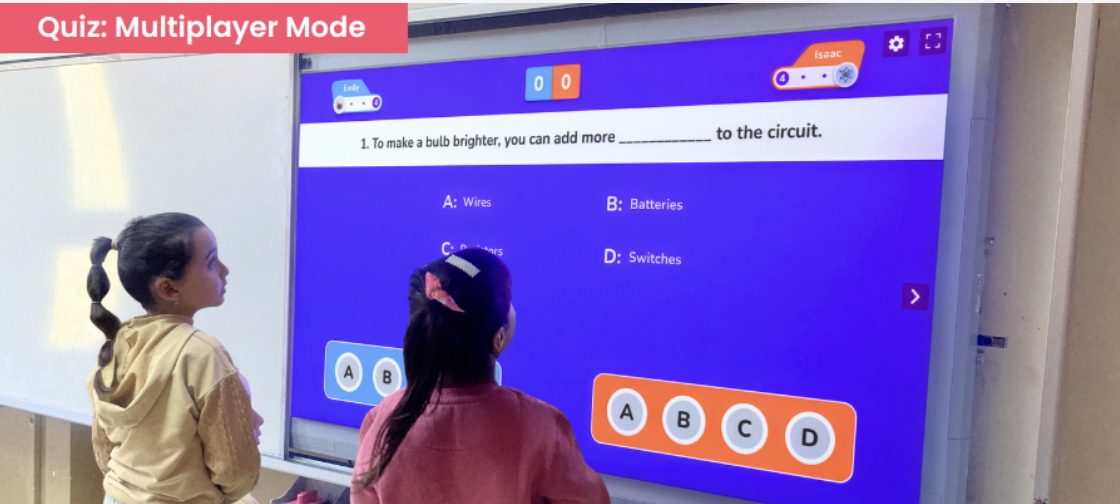
Start with a Quiz!
Kick off your first lessons with engaging multiplayer-mode quizzes on the Twin Educator Platform. With this feature on Twin, you’ll have even the quietest student eager to join.
Try Now >
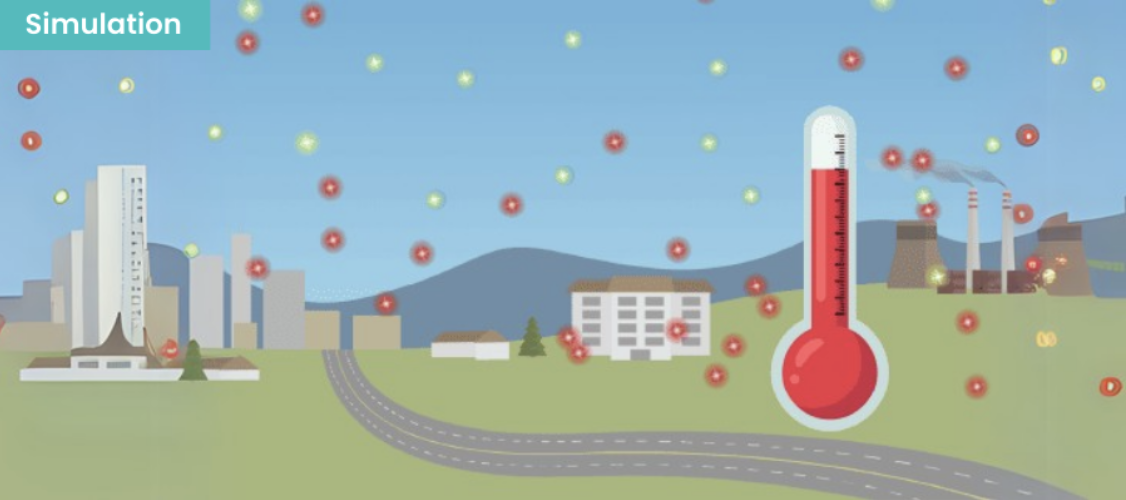
Run a Simulation!
Transform abstract concepts into concrete experiences with simulations from the Twin library. This way, your students will learn topics in a memorable and lasting way.
Try Now >

Engage with Interactive Videos
Keep students engaged with over 5,000 interactive videos that align with your curriculum and the SDGs. Covering everything from AI literacy to tech for good, these videos turn passive viewing into active learning through questions.
Watch Now >
🎁 Get Your Back to School Guide >
Feel free to share this newsletter with any colleagues who might find it helpful—we’re always excited to welcome more educators into our community!
Stay connected with us for the latest updates and insights.
Best regards,
The Twin Science Team 💜
Sep 2, 2025 | Teacher Tips
Twin Educators’ Spotlight: Issue 17
From leaving notes on assignments that strengthen teacher-student connections to interactive challenges and a bold shift in climate education, this week’s newsletter is packed with insights and inspiration. Explore new resources, see how AI is transforming education, and try out engaging activities designed to spark curiosity. Let’s innovate and make learning more impactful—dive in! 🚀
What’s New?
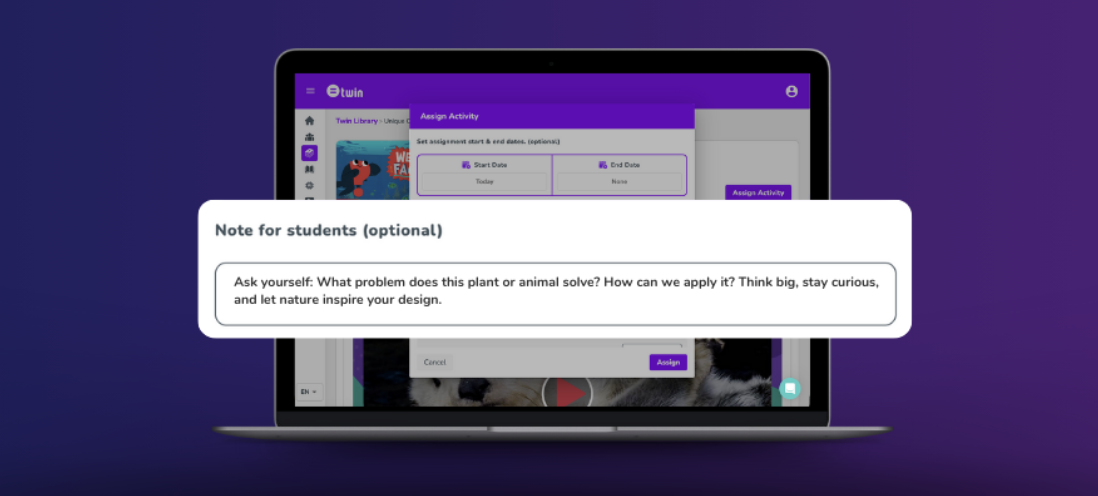
Add Notes to Assignments! 📌
Strengthen the teacher-student connection beyond the classroom! With Twin’s new note for students feature, you can give personalized feedback, share tips, or provide extra guidance while assigning activities.
Try Now >
AI Prompt of the Week

Copy & Paste this Prompt
‘I am a Design and Technology teacher designing a 20-minute classroom activity for 5th graders, aligned with SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), to enhance critical thinking, creativity, and teamwork. In groups of four, students will reflect on their daily and weekly consumption (5 min), identify a problem (5 min), brainstorm a solution (5 min), and present it (5 min). They will use Twin’s Image Forge tool to generate visuals for their presentations, making sustainability concepts more tangible and engaging. The activity should be interactive, age-appropriate, and inspire innovative thinking about responsible consumption at school and home.’
Try AI Assistant Now >
AI in the Classroom

Estonia Sets a New Standard for AI in Education
Estonia is taking a bold step by becoming one of the first countries to integrate AI into its national education system. Starting in 2025, high school students and teachers will gain access to AI-powered tools designed to enhance learning and streamline teaching.
Read More >
Classroom Resources

Wondrous Medicine of Egypt! 🏺
How did the Egyptians harness nature’s wonders for health 5,000 years ago? This interactive video takes your students on a fascinating journey where history and science intertwine. Try it in your classroom and bring learning to life!
Explore Now >
Sustainability Spotlight

Climate Education in Focus 📣
Experts are urging the government to embed climate change across all subjects—not just science and geography. With teachers calling for more support and students facing gaps in climate literacy, could a major curriculum shift be on the horizon?
Read More >
Challenge of the Week

Dancing Popcorns! 🕺
This simple challenge turns kitchen tools into a mini science lab! With vinegar, baking soda, and popcorn kernels, students will create a bubbling reaction that makes the popcorn dance. A perfect way to spark curiosity beyond the classroom!
Explore Now >
Simulation Lab
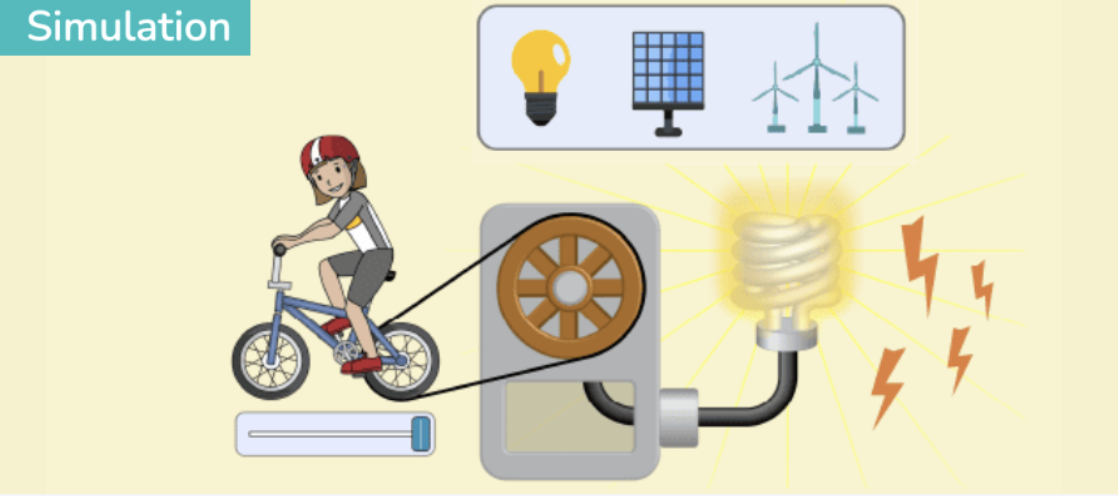
Energy Forms and Changes
Students discover how energy transforms—such as thermal turning into mechanical or electrical energy. Through hands-on experiments, they observe energy transfer, conservation, and efficiency in action.
Try Now >
Community Shoutout
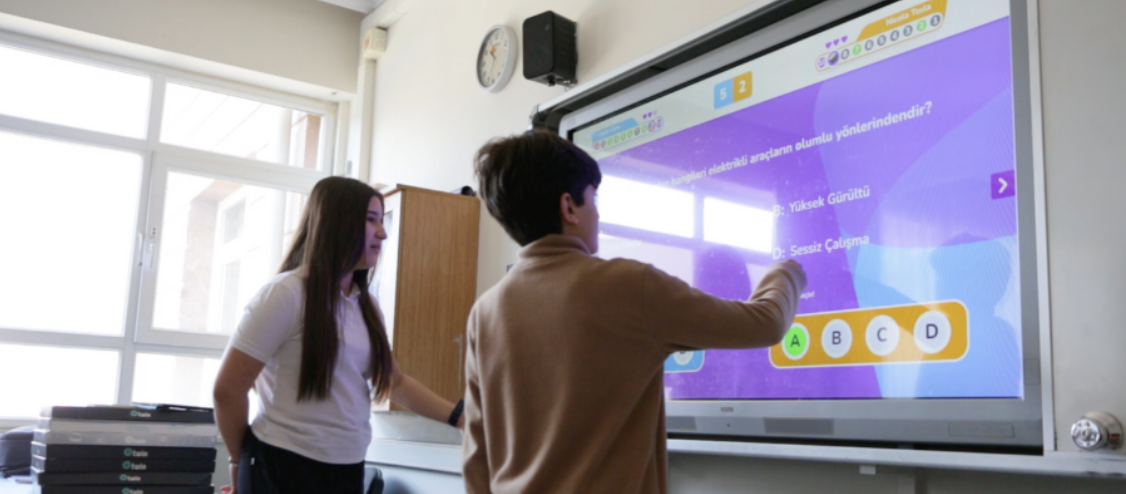

Multiplayer Mode is a Hit!
The new feature on the Twin Educator Platform has quickly gained popularity. Teachers are actively sharing their multiplayer mode experiences in the Twin Educator Community. Now, all quizzes can be played in multiplayer mode with students, turning lessons into exciting learning experiences!
Join the Community >
Behind the Scenes
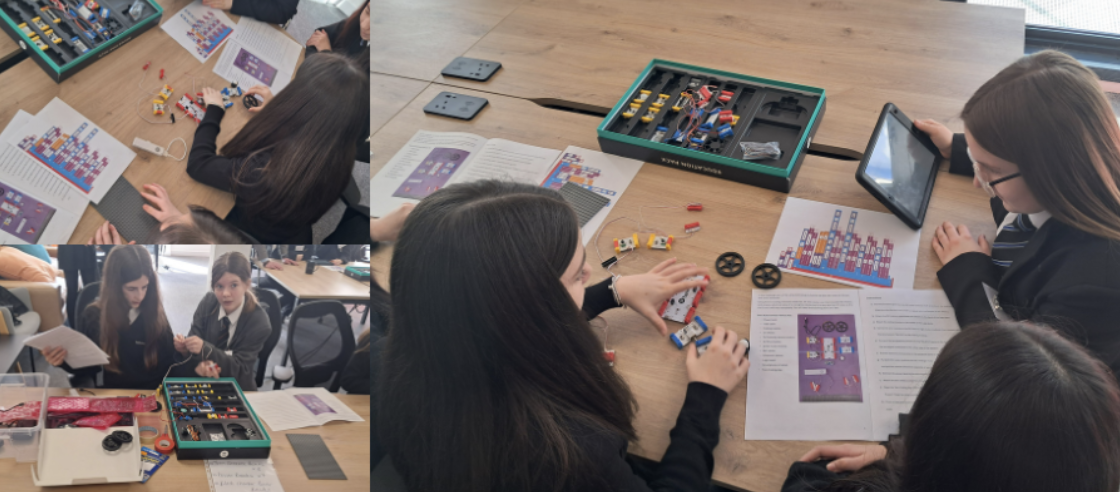

Inspiring Young Minds at ‘Dorset I Belong’!
We were excited to be part of the ‘Dorset I Belong’ conference, where 100+ students explored robotics and coding through our Twin Robotics & EV Cars workshop with Sarah Broughton from Shaftesbury School. A hands-on experience igniting curiosity and innovation!
Learn More >
Feel free to share this newsletter with any colleagues who might find it helpful—we’re always excited to welcome more educators into our community!
Stay connected with us for the latest updates and insights.
Best regards,
The Twin Science Team 💜

Sep 2, 2025 | Teacher Tips
Twin Educators’ Spotlight: Issue 27
The AI revolution in the classroom begins with the teacher. This week on the Twin Educator Platform, a world of discovery awaits—from AI-powered reading comprehension tools and student voice-controlled projects to biomimicry content inspired by nature. As technology evolves rapidly, we navigate it with the wisdom of life, because real transformation happens when teachers like you give meaning to innovation. Enjoy reading! 🌱

Bringing AI to the Classroom Starts with Teacher
Our advisory board member, Mutlu Cukurova from UCL reveals that successful AI adoption depends not on the tool—but on the teacher. His latest research highlights the importance of trust, support, and clear ethics to ensure AI empowers rather than replaces educators.
Read More >
💻 Highlights on Twin
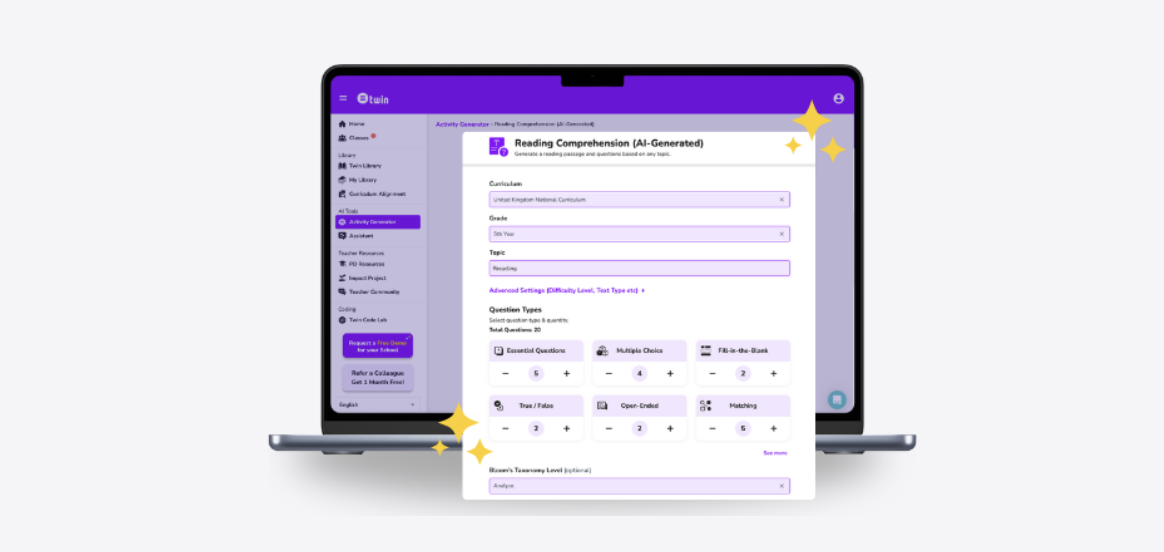
Reading Comprehension (AI-Generated) ✨
Generate fully customized reading texts and worksheets in seconds—tailored to curriculum, grade level, and language complexity. Select everything from word count to Bloom’s Taxonomy level. Design reading experiences that meet your students exactly where they are.
Try Now >
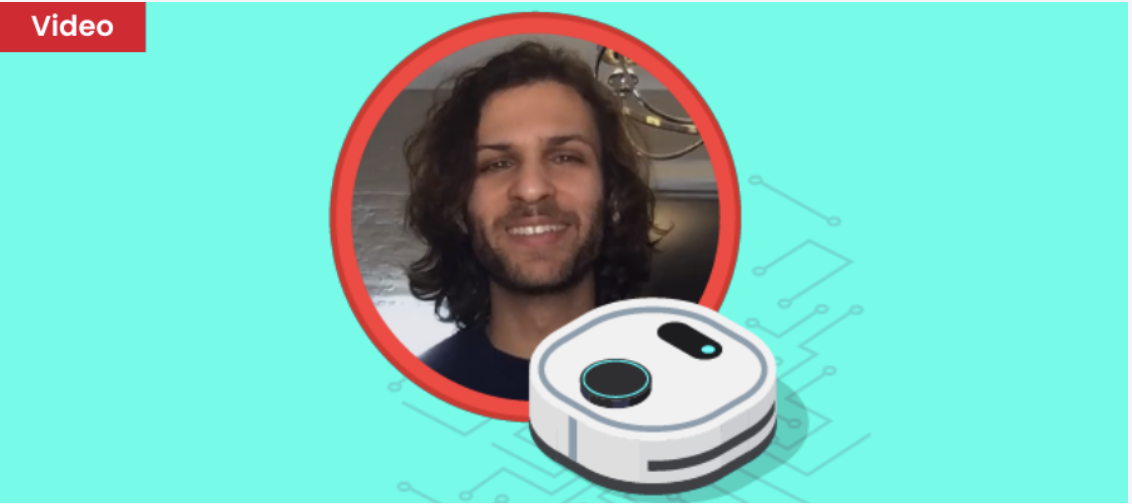

🤖 What Is Artificial Intelligence?
In this interactive video, students dive into the basics of AI—how machines learn, adapt, and make decisions using data. With everyday examples like smart vacuum cleaners, the concept of AI becomes engaging, relatable, and fun to explore!
Watch Now >
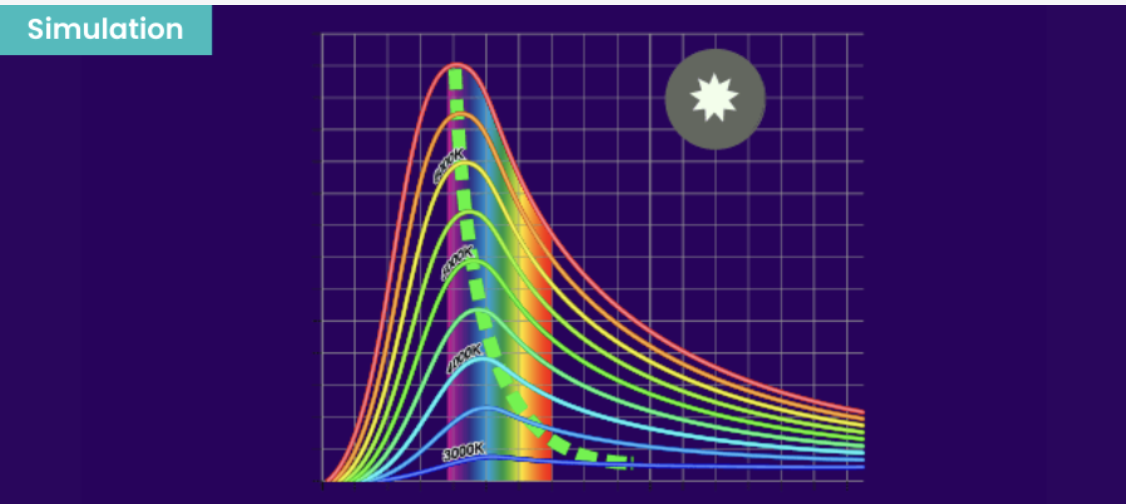
Blackbody Spectrum
Explore thermal radiation with your students through this hands-on simulation! Perfect for ages 9–13, it combines physics and sustainability in a fun, educational experience.
Try Now >
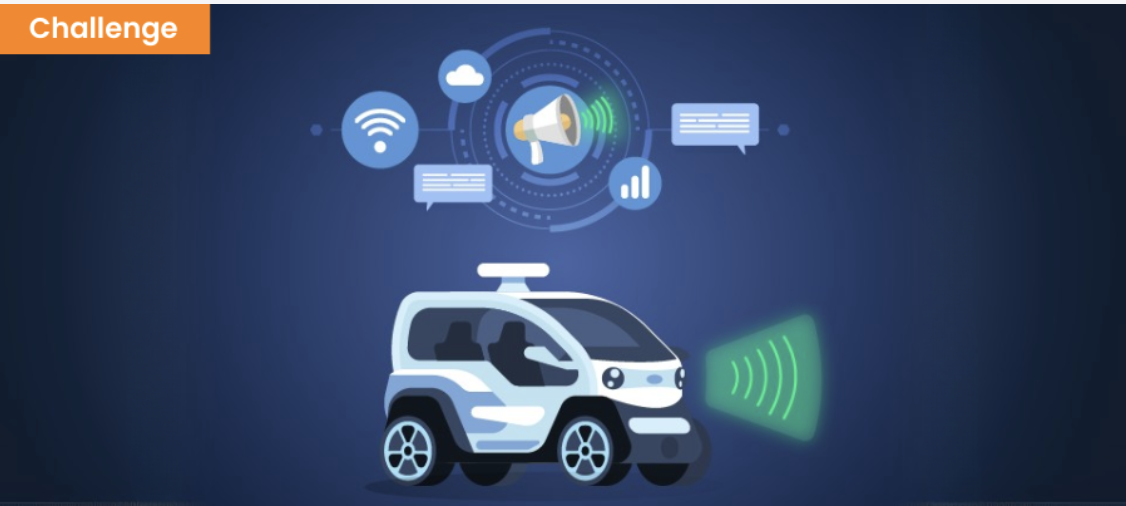

🗣️ Sound Controlled Vehicle
Students design a vehicle that responds to their own voice! Using the Twin Coding App and modules, this hands-on challenge introduces voice recognition and control systems that serve diverse user needs.
Try Now >

Copy & Paste this Prompt
‘Design a simple and fun game that introduces the concept of artificial intelligence to my 4th grade students. The game should last no longer than 20 minutes and should allow each of the 20 students in my classroom to participate and reflect on their experience. Clearly explain the step-by-step activity flow. Also include the learning outcomes the game is expected to achieve.’
Try AI Assistant Now >
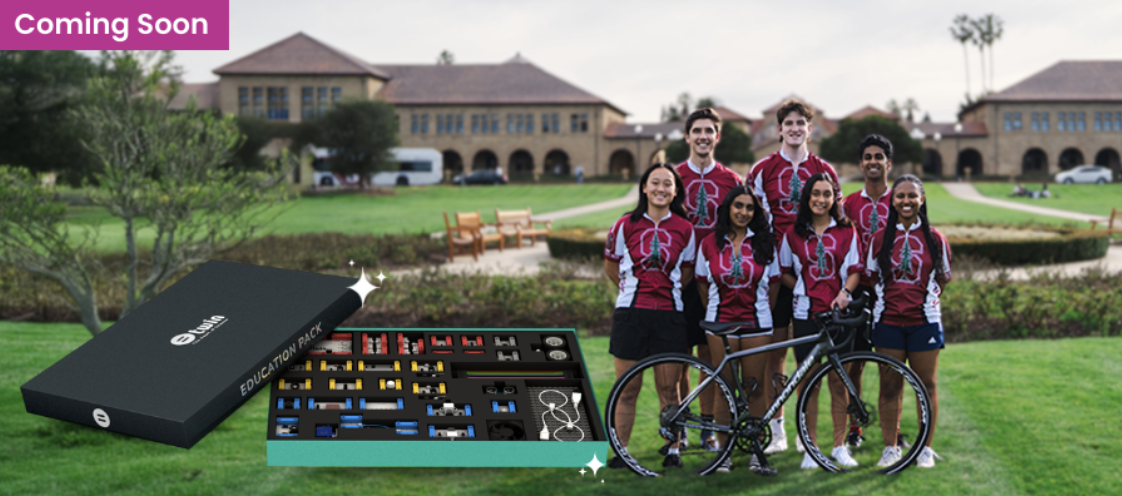

🚴♀️ A Cross-Country STEM Journey Begins!
The Stanford Spokes team is hitting the road with Twin kits! From San Francisco to Washington, D.C., they’ll spark curiosity in over 250 students through hands-on STEM workshops during their 10-week bike journey across the U.S.
Follow Them >
🧑🏫 From the Twin Teacher Community
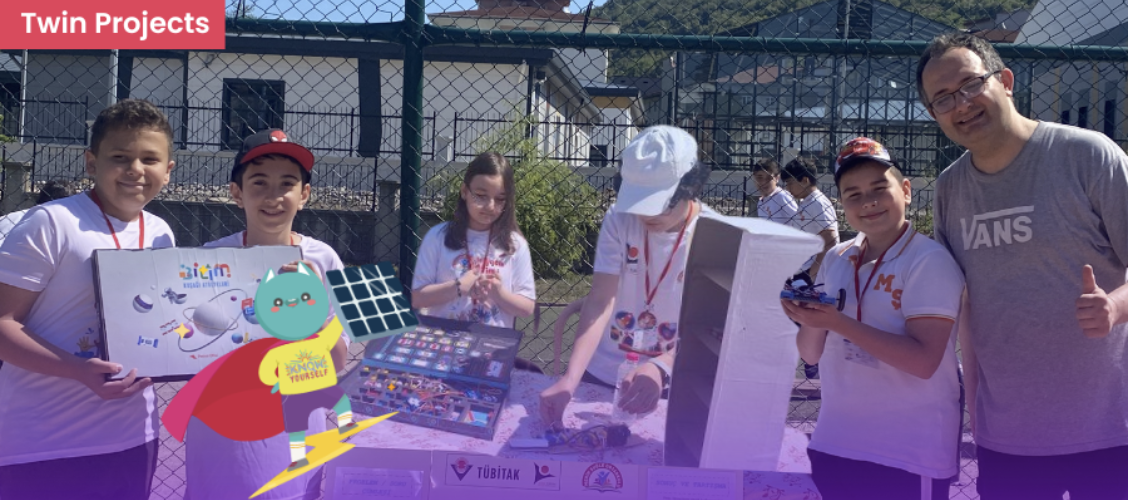

The Future with the Light of Science!
An inspiring update from our teacher A. Can Şimşek! At Merih Şuğle Middle School, the TÜBİTAK 4006 Science Fair and Eco-School event became a joyful celebration of student creativity. Projects built using Twin STEM Kits proudly showcased how double-winged students are turning scientific curiosity into real-world innovation.
Join Twin Educator Community >

The Education of Little Tree | Forrest Carter
Recommended by our inspiring teacher Özgül, The Education of Little Tree is a heartfelt story that goes beyond teaching facts—it invites us to live and feel learning. Woven with values, nature, and meaningful connections, it’s a journey of the heart. Calling it “a book to be lived, not explained,” her recommendation beautifully mirrors our vision of raising compassionate & competent generations.
Join Twin Educator Community >

Interstellar – Christopher Nolan
Teacher Neslihan F. Göknar reflects on Interstellar’s powerful scene where “love transcends time and space,” reminding us that education, too, creates an impact that travels across years and distances. The inspiration you give may echo long after the classroom.
Join Twin Educator Community >
📣 Key Headlines for Educators

What Can AI Really Do?
A new OECD analysis categorizes human abilities into 5 levels, revealing that today’s AI performs well in tasks like summarizing information—but still struggles in uncertain, real-world situations. So how might this shape the future of education and the workforce?
Read More >

Strengthening Education Through Safe School Clubs
In Tanzania, Safe School Clubs led by passionate teachers like Christina Kaduri are transforming classrooms into spaces of trust, confidence, and moral growth. These clubs not only reduce absenteeism but also empower students to thrive beyond academics. So how can we support learners’ growth beyond the classroom?
Read More >

Clean Energy Transformation in UK Schools
Feversham Primary Academy has become one of the pioneering schools in the UK’s clean energy transformation. With newly installed solar panels, the school is expected to save around £13,000 annually on energy costs. These savings will be directly reinvested into resources and programs for students.
Read More >
Feel free to share this newsletter with any colleagues who might find it helpful—we’re always excited to welcome more educators into our community!
Stay connected with us for the latest updates and insights.
Best regards,
The Twin Science Team 💜

Aug 31, 2025 | Teacher Tips
Twin Education Spotlight: Issue 24
Can AI close the learning gap—or widen it further? This week’s stories remind us that the future of education depends on how we use today’s tools. From planting a single tree to reforest a land, to planting an idea that can change a classroom—transformation begins with small, meaningful steps.
At Twin, we believe science guided by empathy can bring both opportunity and balance. That’s why we build tools that not only boost learning, but also bridge global divides—with educators, students, and partners like Stanford by our side. Let’s keep growing together. Enjoy the read! 🌱
💻 Highlights on Twin
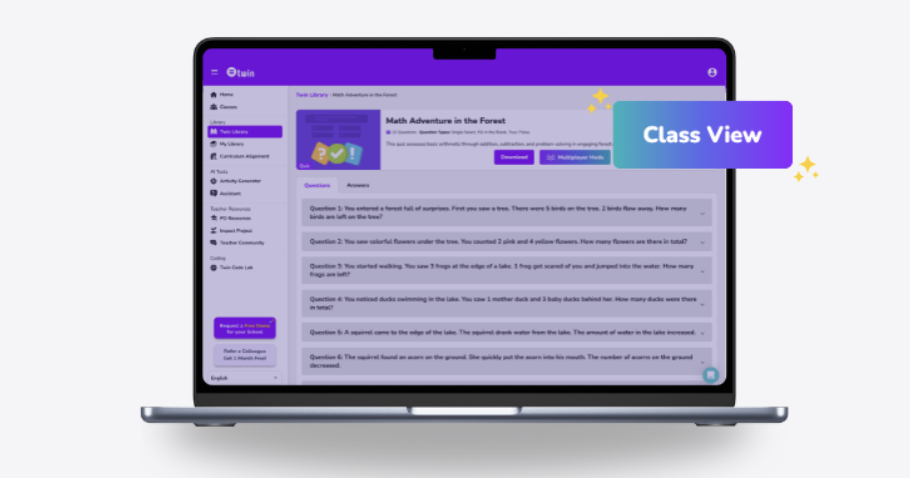
🌟 A New Favourite in the Quizzes Tab!
There’s a new addition to one of the most loved areas of the Twin platform: the Quizzes tab! Alongside Multiplayer Mode, you’ll now find Class View—a feature that lets you run quizzes directly on your smartboard and present each question live to your students. Make your lessons more engaging, competitive, and fun!
Try Now >
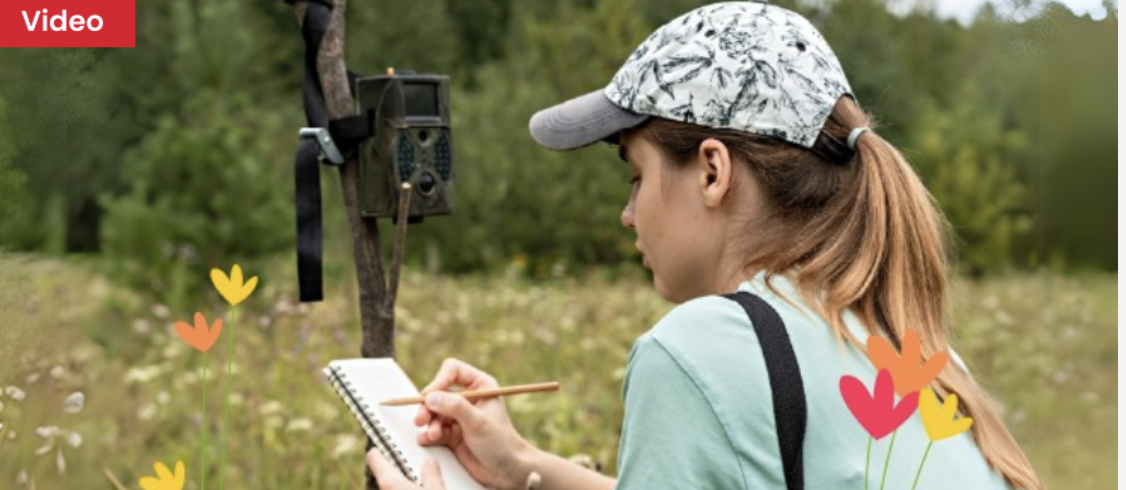

Content of the Week: Sound Sensors in Forests
What can a forest tell us—if we know how to listen? In this video, students will discover how zoologists use sound sensors to study animal behavior, explore sound waves, and unlock hidden patterns in nature. A perfect blend of biology, physics, and curiosity!
Explore Now >

Simulation Lab: Greenhouse Effect 🌡️
Why is our planet getting warmer? In this interactive simulation, students explore how greenhouse gases trap heat and impact Earth’s climate. Let your class investigate, test, and reflect on real-world sustainability through science in action.
Try Now >
Challenge of the Week: Plant a Tree 🌱

Inspired by Sebastião Salgado—who helped turn barren land into a thriving forest—your students are invited to plant one small tree and witness how change begins. This week, assign your class a mission: plant a tree, take a photo, and leave a mark of hope for the future.
Try Now >
PS: For those curious about the full story, we recommend the film The Boy Who Harnessed the Wind!

Copy & Paste this Prompt
‘Imagine you’re a 3rd grade classroom teacher. Design a 20-minute role-playing activity that helps students practice empathy and cooperation. The game should be simple, fun, and engaging for young learners. Include clear roles, a relatable scenario (like a classroom, playground, or neighbourhood), and specific actions students can take to show empathy and work together. Make sure every child has a chance to participate and reflect briefly at the end.’
Try AI Assistant Now >

7 Students, 7 Bikes, and Twin STEM Kits on the Road
This summer, seven Stanford students will bike across the U.S. from San Francisco to Washington, D.C.—carrying more than just backpacks. With Twin STEM kits, their mission is to spread STEM for Sustainability and make hands-on learning accessible to every child they meet. Stay tuned for more updates on this journey!
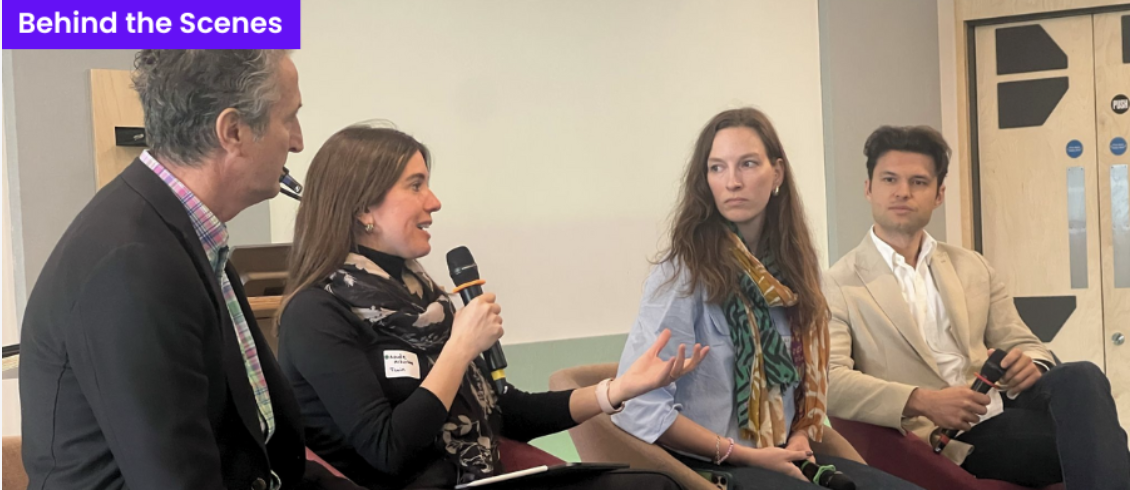

Behind the Scenes: Social Impact to Sustainability
At the TRUK Accelerator London Chapter Launch, Twin CEO Asude Altıntaş Güray shared her experience advancing holistic STEM education through award-winning social innovation. Drawing from her journey, she highlighted how technology and education can empower underserved communities and drive long-term impact. In a room filled with purpose-driven founders, Twin’s mission stood out as a powerful example of how learning can become a force for equity and sustainability.
Read more >
🧑🏫 From the Twin Teacher Community
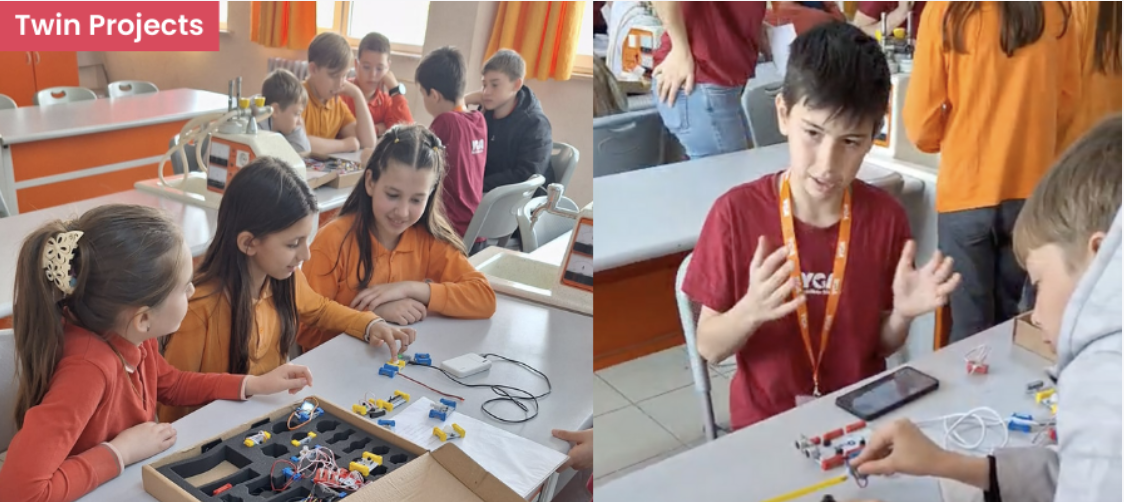

Those Who Know Twin, Teach It to Others!
Our teachers Bahar Özhan Tan and Özlem Genç Mutlu have launched a peer learning movement that’s reaching beyond their own schools! With the help of middle and high school volunteers who know how to use Twin STEM kits, they’re now running workshops in five more schools across their district.
Join Twin Educator Community >
PS: Our teacher Bahar has a movie recommendation just for you!
From the Teacher’s Shelf: Big Friends

Our teacher Aslı Gökgöz recommends Big Friends by Linda Sarah—a heartfelt story that gently explores whether there’s room for a third person in a two-person friendship. It’s a perfect P4C resource to spark thoughtful discussions on emotions like jealousy, as well as imagination and collaboration. The story also shows how cardboard boxes become whole worlds through creativity—just like students can with Twin modules and a little imagination!
Join Twin Educator Community >
Educators’ Watch Pick: Tuesdays with Morrie

Recommended by our teacher Bahar Özhan Tan, Tuesdays with Morrie is a heartfelt story where a retired professor and his former student reconnect to rediscover what truly matters in life. A gentle reminder that even beyond the classroom, teachers continue to shape lives.
Join Twin Educator Community >
📣 Key Headlines for Educators

🎯 Early Insight, Smarter Teaching
New research from Stanford HAI shows that just 2 to 5 hours of learning data can help predict whether a student will struggle or excel in future assessments. This means teachers can intervene earlier, tailor instruction more effectively, and support students before challenges turn into learning gaps.
Read More >
Sustainability Spotlight: Early Holiday, More Fans 🌡️
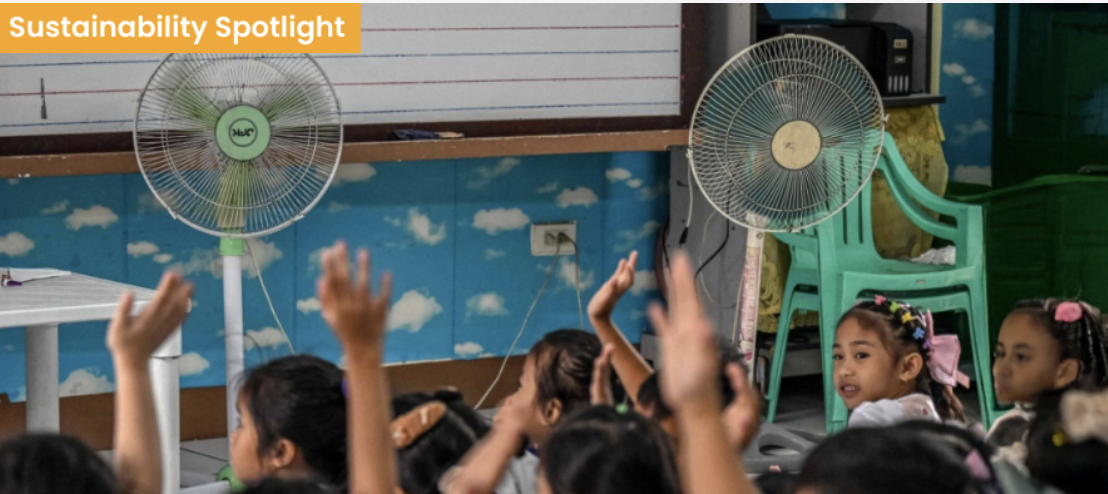

Soaring temperatures in the Philippines forced millions of students out of school last year. Now, schools are shifting schedules, shortening lessons, and adding fans and water stations to keep learning going—even in extreme heat. This is what climate adaptation looks like in classrooms with limited resources, led by teachers determined to protect learning and wellbeing.
Read More >
Where Roots Remember and Trees Return
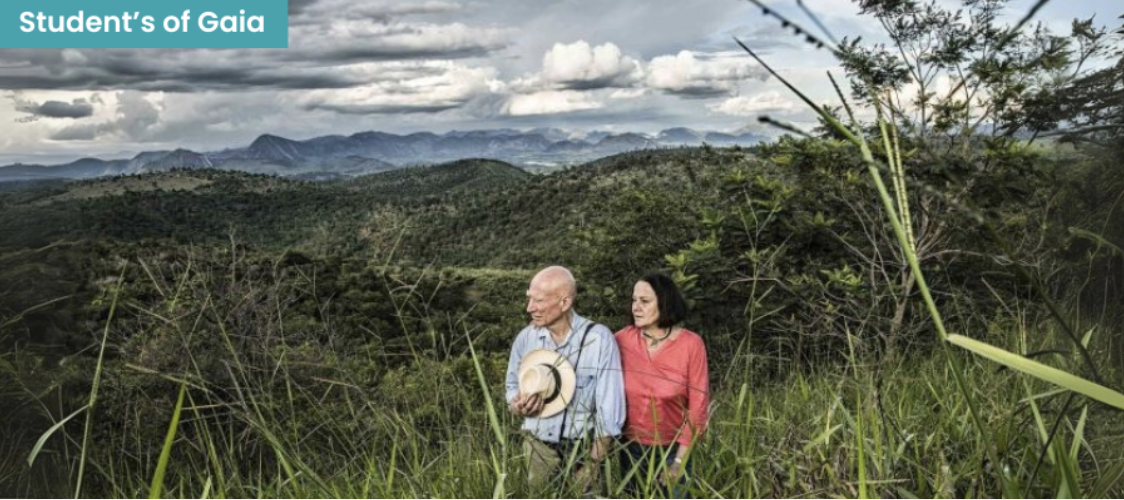

When renowned photographer Sebastião Salgado returned to his childhood farm, he found not the rainforest of his memories—but a barren land. Together with his wife Lélia, he began reforesting the land, planting nearly 3 million trees and founding Instituto Terra. Today, the reserve is not only a flourishing forest, but also a space for environmental education—where local children, called Terrinhas, learn about water cycles, recycling, and the power of restoration.
Read More >
How AI Will Divide the Best From the Rest

AI is boosting productivity across every field—but not equally. Research shows that those with access to these technologies are advancing rapidly, while the gap grows deeper for underserved communities. We believe education should offer equal opportunities to every child. Through initiatives like the World Science Movement, Twin is working to bridge this divide—bringing cutting-edge technology to children around the world.
Read More >
PS: Want to see how Stanford’s biking students and Twin are helping reduce the learning gap? You’re just four scrolls away!
Feel free to share this newsletter with any colleagues who might find it helpful—we’re always excited to welcome more educators into our community!
Stay connected with us for the latest updates and insights.
Best regards,
The Twin Science Team💜
















































